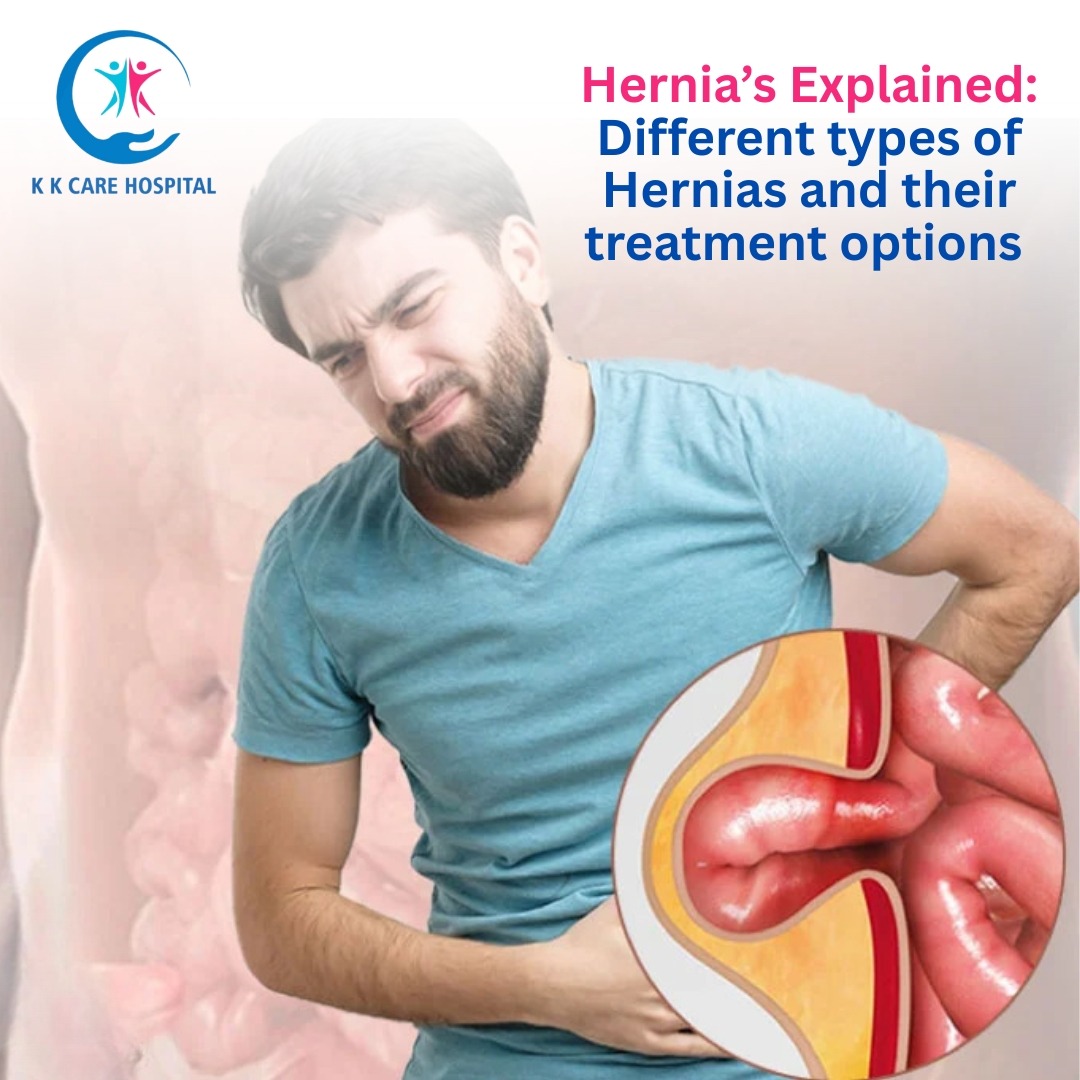
A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue pushes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. Hernias are a common medical condition affecting people of all ages, and they can occur in various parts of the body. Understanding the types of hernias, their symptoms, and the available treatment options is essential for timely management and preventing complications.
What is a Hernia?
Hernias typically occur in areas where the muscle wall is naturally weaker, such as the abdomen or groin. Factors such as heavy lifting, chronic coughing, obesity, or age-related muscle weakness can increase the risk of developing a hernia. While some hernias are painless and grow slowly, others can cause discomfort and lead to serious complications like strangulation, where blood supply to the trapped tissue is cut off.
Common Types of Hernias
Understanding the different types of hernias helps in identifying symptoms and choosing appropriate treatment. The most common types include:
- Inguinal Hernia
The inguinal hernia is the most common type, occurring in the groin area. It is more prevalent in men than women. Symptoms may include a bulge in the groin, discomfort during physical activity, or pain when bending or lifting. Inguinal hernias may be direct or indirect, depending on their position relative to the inguinal canal.
- Femoral Hernia
Femoral hernias occur just below the groin, near the upper thigh. They are more common in women and can often be mistaken for inguinal hernias. Symptoms include a small lump in the upper thigh, which may cause discomfort or pain when standing or walking.
- Umbilical Hernia
An umbilical hernia occurs around the navel and is common in infants and obese adults. It may present as a soft bulge near the belly button and often becomes noticeable when the person coughs or strains. In infants, these hernias often close naturally, but in adults, surgical repair may be needed.
- Hiatal Hernia
A hiatal hernia occurs when a part of the stomach pushes up into the chest through the diaphragm. Unlike other hernias, hiatal hernias often do not present as visible lumps. Symptoms can include heartburn, regurgitation, chest pain, and difficulty swallowing. Lifestyle changes and medication are first-line treatments, though surgery may be required in severe cases.
- Incisional Hernia
Incisional hernias develop at the site of a previous surgical incision. They occur when the muscle wall does not heal properly after surgery, creating a weak spot. Symptoms include a bulge near the surgical scar and discomfort, especially when lifting or coughing.
- Other Types
Less common hernias include epigastric hernias (upper abdomen), spigelian hernias (side of the abdominal wall), and obturator hernias (pelvic region). These hernias are rarer but require medical attention due to the risk of complications.
Symptoms of Hernias
Hernias may present differently depending on their type and location, but common symptoms include:
- A visible bulge or lump in the affected area
- Pain or discomfort, especially during physical activity or lifting
- Weakness, pressure, or heaviness in the abdomen or groin
- Swelling around the testicles (inguinal hernia in men)
- Digestive issues or heartburn (hiatal hernia)
Some hernias may remain asymptomatic for years, while others can progress rapidly, requiring urgent care.
Treatment Options for Hernias
Treatment for hernias depends on the type, size, symptoms, and risk of complications. The main options include:
- Watchful Waiting
For small, asymptomatic hernias, doctors may recommend monitoring the condition. Regular check-ups ensure that the hernia does not grow or cause complications. Patients are advised to avoid heavy lifting and maintain a healthy weight.
- Surgical Repair
Surgery is the definitive treatment for hernias that are large, painful, or at risk of complications. There are two main surgical approaches:
- Open Hernia Surgery
In open surgery, the surgeon makes an incision near the hernia site, pushes the protruding tissue back, and strengthens the weak area with stitches or surgical mesh. Open surgery is effective for most types of hernias and has a high success rate.
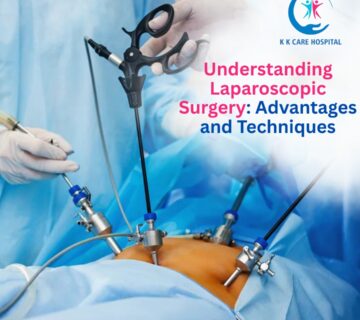
- Laparoscopic Hernia Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive technique involving small incisions and the use of a camera and specialized instruments. This approach offers faster recovery, less pain, and minimal scarring. It is commonly used for inguinal, umbilical, and incisional hernias.
- Lifestyle and Supportive Measures
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes can help manage hernia symptoms and prevent progression:
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the abdominal wall
- Avoid heavy lifting or straining
- Use a hernia belt or truss temporarily for support (not a permanent solution)
- Eat a high-fiber diet to prevent constipation and straining
When to Seek Medical Attention
Immediate medical care is needed if a hernia becomes incarcerated or strangulated, which can be life-threatening. Warning signs include:
- Sudden pain and tenderness at the hernia site
- Redness, swelling, or discoloration over the bulge
- Nausea, vomiting, or fever
Prompt surgical intervention is critical to prevent tissue damage and other complications.
Conclusion
Hernias are a common condition, but with proper awareness and timely treatment, complications can be avoided. Understanding the different types of hernias, recognizing symptoms, and knowing the available treatment options can empower patients to make informed decisions about their health.
At KK Care Hospital, our experienced surgeons specialize in both open and laparoscopic hernia repairs, ensuring safe, effective, and minimally invasive treatment tailored to each patient. If you notice a bulge, pain, or discomfort, consult our specialists to receive personalized care and guidance for the best outcomes.




No comment