In recent years, laparoscopic surgery has revolutionized the field of modern medicine. Often referred to as minimally invasive surgery, it allows doctors to perform complex procedures through small incisions, offering patients faster recovery and minimal discomfort compared to traditional open surgery. This article explores what laparoscopic surgery is, its advantages, and the techniques used, helping patients make informed decisions about their treatment.
What is Laparoscopic Surgery?
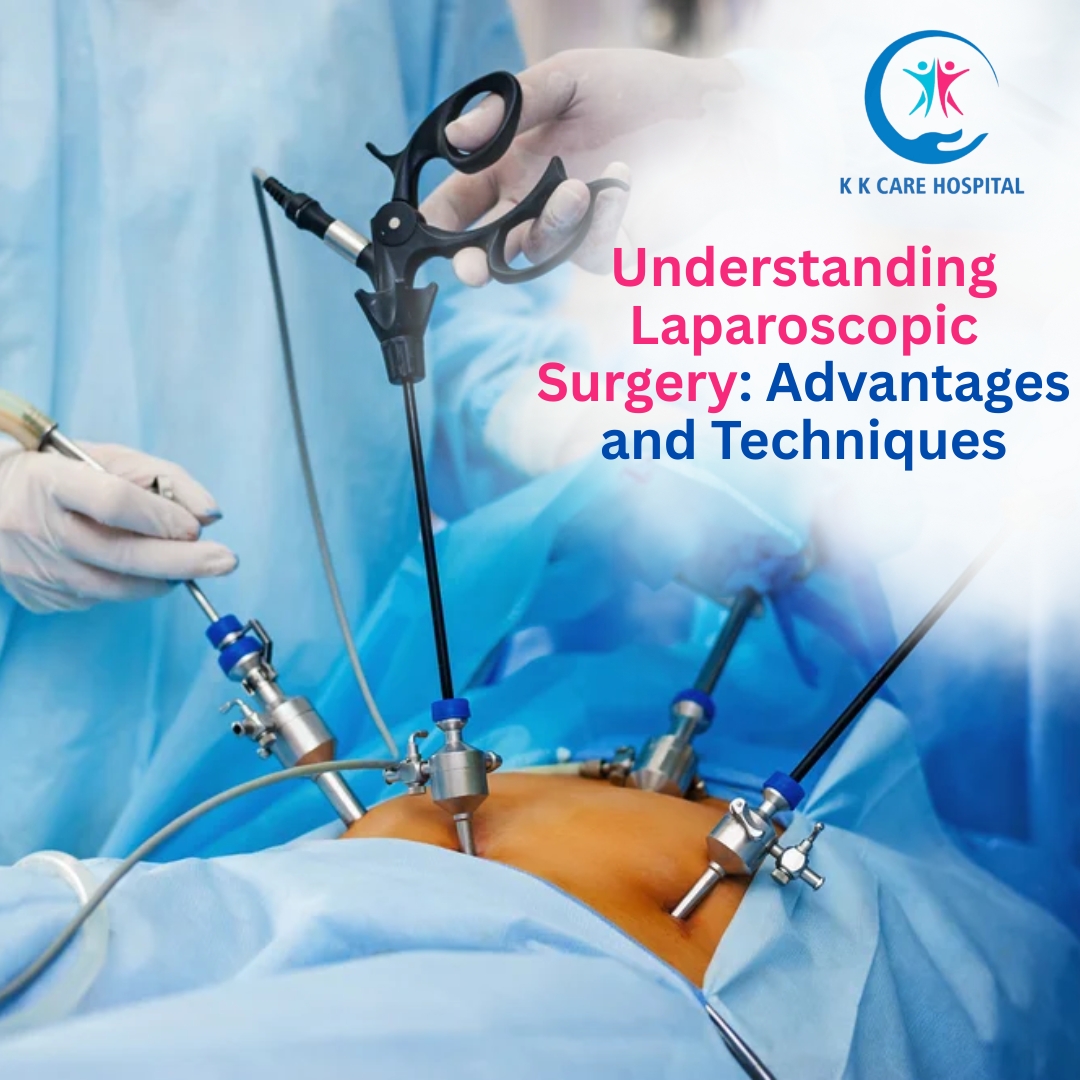
Laparoscopic surgery is a technique in which surgeons operate through small incisions, typically ranging from 0.5 to 1.5 cm, using specialized instruments and a camera called a laparoscope. The laparoscope transmits high-definition images of the internal organs to a monitor, giving the surgeon a clear view while avoiding large incisions.
Unlike conventional surgery, where a large incision is made to access the affected area, laparoscopic surgery allows the surgeon to work with precision through tiny openings. This minimally invasive approach is commonly used for procedures involving the gallbladder, appendix, hernia, uterus, and gastrointestinal tract, among others.
Advantages of Laparoscopic Surgery
The benefits of laparoscopic surgery have made it a preferred option for many patients and doctors worldwide. Here are some key advantages:
- Smaller Incisions and Less Scarring
Since laparoscopic surgery uses small cuts, patients experience minimal scarring. The cosmetic outcome is better compared to open surgery, which often leaves larger and more noticeable scars.
- Reduced Pain and Discomfort
Smaller incisions mean less trauma to the body’s tissues. As a result, patients generally experience less post-operative pain, reducing the need for strong pain medications.
- Faster Recovery and Shorter Hospital Stay
One of the most significant benefits is the quicker recovery time. Patients often return to their normal routine within a few days to a week, while traditional surgery may require weeks of recovery. Shorter hospital stays also reduce the risk of hospital-acquired infections.
- Lower Risk of Complications
The minimally invasive nature of laparoscopic surgery reduces the risk of complications such as infections and hernias. Additionally, enhanced precision helps surgeons perform delicate procedures more safely.
- Better Visualization for Surgeons
The high-definition camera used in laparoscopy provides magnified views of internal organs, enabling surgeons to perform more precise and delicate operations. This can be particularly advantageous in procedures involving complex anatomy.
- Suitable for Various Conditions
Laparoscopic techniques can be applied to a wide range of surgeries, including gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy), appendectomy, hernia repair, hysterectomy, bariatric surgery, and even some cancer treatments. Its versatility makes it a preferred choice in both elective and emergency surgeries.
Techniques Used in Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery involves specialized instruments and techniques to ensure minimal trauma and optimal outcomes. Here are the main steps and techniques:
- Creating Small Incisions
The surgeon makes 1-4 small incisions depending on the procedure. One of these incisions is used to insert the laparoscope, while others accommodate surgical instruments.
- Insufflation of the Abdomen
To create space for surgery, carbon dioxide gas is introduced into the abdominal cavity, inflating it slightly. This separation allows the surgeon to view and access organs more easily.
- Inserting the Laparoscope and Instruments
A laparoscope equipped with a camera is inserted through one incision, transmitting real-time images to a monitor. Specialized instruments are inserted through other small incisions to perform the surgery.
- Performing the Surgery
Using the instruments, the surgeon carefully performs the procedure while watching the monitor. The magnified view allows for precise movements, reducing the risk of damage to surrounding tissues.
- Closing Incisions
After the procedure, the instruments are removed, the gas is released, and the small incisions are closed with sutures or surgical tape. The tiny incisions heal quickly, leaving minimal scarring.
Who is a Candidate for Laparoscopic Surgery?
Laparoscopic surgery is suitable for most patients, but individual suitability depends on factors like overall health, the complexity of the condition, and previous abdominal surgeries. A thorough medical evaluation and imaging tests help the surgeon determine whether a laparoscopic approach is appropriate.
Preparing for Laparoscopic Surgery
Preparation is crucial for a successful laparoscopic procedure. Patients are usually advised to:
- Avoid eating or drinking for several hours before surgery.
- Inform the surgeon about medications, allergies, or existing medical conditions.
- Arrange for someone to assist them post-surgery, as recovery may require temporary support.
Recovery and Post-Operative Care
After laparoscopic surgery, patients can expect:
- Mild discomfort at the incision sites, usually managed with over-the-counter pain medications.
- Gradual return to normal activities within a few days.
- Avoiding heavy lifting or strenuous activity for 2–4 weeks.
- Following the surgeon’s instructions for wound care, diet, and follow-up appointments.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic surgery represents a major advancement in surgical care, offering numerous benefits such as smaller incisions, faster recovery, reduced pain, and lower risk of complications. Understanding the procedure, its advantages, and the techniques involved can help patients make informed decisions about their health.
At KK Care Hospital, our experienced surgical team specializes in a wide range of laparoscopic procedures, ensuring safe, effective, and patient-friendly care. If you are considering surgery, consult our specialists to learn how laparoscopic techniques can improve your recovery and overall outcomes.




No comment